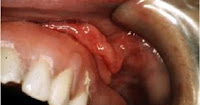
Distal fissures or premolar contact oppose.. middle of the middle third and vice versa
Distal fissures or premolar contact oppose?
A- Middle of the middle third and buccal fissures wider than lingual
B- Cervical line and lingual fissure if wider than buccal
C- middle of the middle third and vice versa***
D- cervical.
-------------------
Premolar tooth is called any tooth that erupts in the space left by a temporary molar. There are a total of 8 premolars, 4 in the jaw and 4 in the maxilla, two on each side respectively. They are located distal to the canine, so that the first premolar is distal to the canine, and distal to the first premolar is the second premolar. They are immediately before the molars.
They are also known by the term bicuspids although this term is incorrect since the second lower premolar has 3 cusps (tricuspid).
Their anatomy allows them to participate with the canines in the tearing of food and with the molars in grinding them. Although they are attributed, mainly, the function of fine grinding and crushing of food.
Upper premolars:
They have a crown with pentagonal shape, greater vestibulopalatin dimension to the mesiodistal. They have two cusps: vestibular, larger and quadrangular in shape, and palatine, smaller.
Your dental contacts are:
- Proximals:
the first superior premolar contacts the superior canine mesially and distally with the second superior premolar. The second upper premolar mesially contacts the first upper premolar and distally with the first upper molar.
- Occlusals:
the mesial slope of the first upper premolar contacts the distal slope of the first lower premolar, the distal slope of the first upper premolar contacts the mesial of the second lower premolar and the mesial slope of the second upper premolar will contact the distal slope of the second lower premolar and the distal of the second upper premolar with the mesial of the lower first molar.
Cusps:
They can have one to two roots, two roots are found more frequently in the first upper premolar. If we have a unique root, it will present a mesial groove. A double curvature in the apical third is very frequent, it has a convergence on the palatal side, it can be seen very clearly if we see it on the occlusal side. The first upper premolar has a crown larger than the second upper premolar, the occlusal face is more asymmetric in the first upper premolar.
Lower premolars:
They are located distally with respect to the lower canine. It is not uncommon to find agenesis (absences) or supernumerary teeth. The first lower premolar has a pentagonal shape from an occlusal view. It has two cusps: lingual and vestibular, this one of greater size. A differential feature of the occlusal face of the first lower premolar is that the vestibular and lingual central triangular ridges continuously cross the occlusal face, so we speak of a single crest, the transverse crest.
Your dental contacts are:
- Proximals:
the first lower premolar contacts mesially with the lower canine and distally with the second lower premolar.
- Occlusals:
contact the distal slope of the upper canine and the mesial slope of the first upper premolar.
Both lower premolars have a great similarity although the following differences are found:
- The root of the second lower premolar is narrow and a bit narrow compared to the other upper premolars, and is longer than that of the first lower premolar.
- There are two types of lower premolar seconds, one with two cusps, one lingual and one vestibular, and another with 3 cusps, two lingual and one vestibular.
- The vestibular cusp of the second lower premolar is less pointed than that of the first lower premolar, with the cusp slopes less inclined.
A- Middle of the middle third and buccal fissures wider than lingual
B- Cervical line and lingual fissure if wider than buccal
C- middle of the middle third and vice versa***
D- cervical.
-------------------
Premolar tooth is called any tooth that erupts in the space left by a temporary molar. There are a total of 8 premolars, 4 in the jaw and 4 in the maxilla, two on each side respectively. They are located distal to the canine, so that the first premolar is distal to the canine, and distal to the first premolar is the second premolar. They are immediately before the molars.
They are also known by the term bicuspids although this term is incorrect since the second lower premolar has 3 cusps (tricuspid).
Their anatomy allows them to participate with the canines in the tearing of food and with the molars in grinding them. Although they are attributed, mainly, the function of fine grinding and crushing of food.
Upper premolars:
They have a crown with pentagonal shape, greater vestibulopalatin dimension to the mesiodistal. They have two cusps: vestibular, larger and quadrangular in shape, and palatine, smaller.
Your dental contacts are:
- Proximals:
the first superior premolar contacts the superior canine mesially and distally with the second superior premolar. The second upper premolar mesially contacts the first upper premolar and distally with the first upper molar.
- Occlusals:
the mesial slope of the first upper premolar contacts the distal slope of the first lower premolar, the distal slope of the first upper premolar contacts the mesial of the second lower premolar and the mesial slope of the second upper premolar will contact the distal slope of the second lower premolar and the distal of the second upper premolar with the mesial of the lower first molar.
Cusps:
They can have one to two roots, two roots are found more frequently in the first upper premolar. If we have a unique root, it will present a mesial groove. A double curvature in the apical third is very frequent, it has a convergence on the palatal side, it can be seen very clearly if we see it on the occlusal side. The first upper premolar has a crown larger than the second upper premolar, the occlusal face is more asymmetric in the first upper premolar.
Lower premolars:
They are located distally with respect to the lower canine. It is not uncommon to find agenesis (absences) or supernumerary teeth. The first lower premolar has a pentagonal shape from an occlusal view. It has two cusps: lingual and vestibular, this one of greater size. A differential feature of the occlusal face of the first lower premolar is that the vestibular and lingual central triangular ridges continuously cross the occlusal face, so we speak of a single crest, the transverse crest.
Your dental contacts are:
- Proximals:
the first lower premolar contacts mesially with the lower canine and distally with the second lower premolar.
- Occlusals:
contact the distal slope of the upper canine and the mesial slope of the first upper premolar.
Both lower premolars have a great similarity although the following differences are found:
- The root of the second lower premolar is narrow and a bit narrow compared to the other upper premolars, and is longer than that of the first lower premolar.
- There are two types of lower premolar seconds, one with two cusps, one lingual and one vestibular, and another with 3 cusps, two lingual and one vestibular.
- The vestibular cusp of the second lower premolar is less pointed than that of the first lower premolar, with the cusp slopes less inclined.




%20tube%20has%20stopped%20draining..%20Notify%20the%20physician.jpg)